Florian Beaurain
SMQ engineer
Master 2 « Medical Device: Design and assessment » (University of Lille, France)
Objective: Comparison of GNRB® versus MRI in the diagnosis of different patterns of anterior cruciate ligament tears.
Requirements: Patients operated for ACL tears or ACL tears + meniscus.
Exclusion Criteria: all patients without isolate ACL tears (without other ligament and bone injuries), patients were not get primary surgery.
Collection of Data
Database of Dr Henri ROBERT (surgeon, specialist on ACL surgery: Operative report, MRI (1.5 T) report and GNRB database for all patients).
Group of Patients
2 groups:
- Patients with complete ACL tears
- Patients with partial ACL tears
Statistical Test
We use sensibility like an indicator for average method
Binary Criteria: ACL tears (partial or complete)
Acceptability
For MRI report, if it required interpretation, it shall be null. It must be clearly mentioned complete or partial tears in the conclusion report.
For GNRB, if delta for both knees >3 mm = complete tears and if 1.5 mm ≤ delta <3 mm, partial tears.
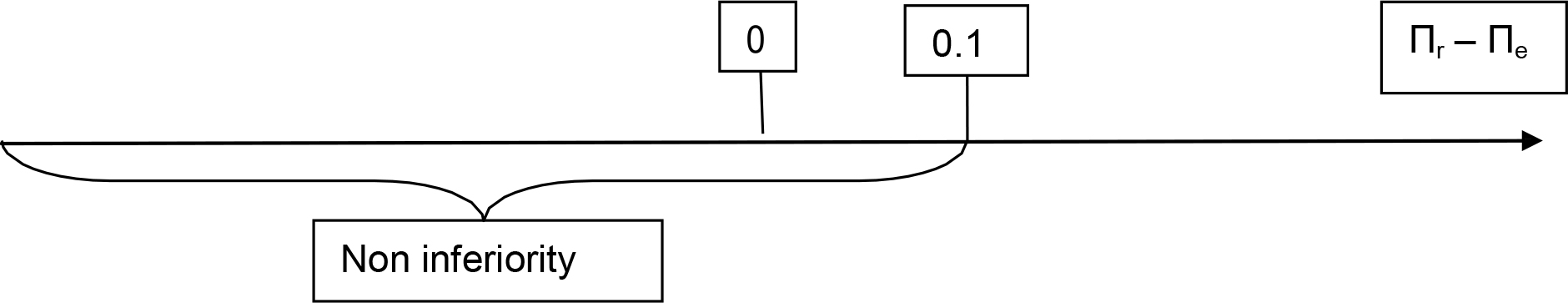
Non Inferiority Test
Estimate value: Pr (MRI’s sensibility [1]) by Πr = 0.57
Estimate value: Pe (GNRB’s sensibility [2,3]) by Πe = 0.84
It set α = 5 % unilateral, β = 10 % and δ = 10%.
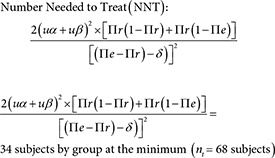
For estimation by confidence interval (CI) of difference of proportions
With Pe = GNRB’s sensibility and Pr = MRI’s sensibility and Ne = Nr
–nr, ne ≥ 30
–nrpr, nr(1–pr), nepe, ne(1–pe) ≥ 5
![]()
Pattern
Difference of Proportions Test
– Difference test at δ ≠ 0
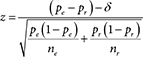
Results
This study was performed on data from previous years and two years before for 200 operated patients in total. After exclusion of 64 medical files (one of the 3 data is missing: GNRB, MRI or arthroscopic report), 62 tears were partial and 74 complete with arthroscopy report [Table 1, 2, 3].
Table 1: Table of IRM’s and GNRB’s sensibility with arthroscopy for reference.
|
|
MRI vs Arthroscopy for Complete ACL |
MRI vs Arthroscopy for Partial ACL |
GNRB vs Arthroscopy for Complete ACL |
GNRB vs Arthroscopy for Partial ACL |
|
Number |
47 |
22 |
45 |
46 |
|
Number of Subject |
62 |
74 |
62 |
74 |
|
Sensibility |
0,76 |
0,30 |
0,73 |
0,62 |
Table 2: Sensibility and specificity of GNRB in the literature.
|
|
Complete ACL |
|
Partial ACL |
|
|
|
Sensibility |
Specificity |
Sensibility |
Specificity |
|
Robert H [5] |
70% |
99 % |
80% |
87% |
|
Klouche S [3] |
92% |
96 % |
92% |
98% |
|
Di Ioro A |
|
|
72% |
85% |
|
Lefevre N |
84% |
81% |
87% |
87% |
|
Beldame J |
62% |
75% |
|
|
|
Beaurain F |
73% |
|
62% |
|
Table 3: Sensibility of MRI in the literature.
|
|
Complete ACL |
Partial ACL |
|
Beldame J [1] |
57% |
|
|
Steltzlen C [4] |
|
32% |
For complete tears, MRI’s sensibility was 0.76 and GNRB’s sensibility 0.73. For partial tears, MRI’s sensibility was 0.30 and GNRB’s sensibility 0.62.
For Complete Tears
For estimation by Confidence Interval (CI) of difference of proportions
Conditions for application are verified.

For Partial Tears [4]
For estimation by Confidence Interval (CI) of difference of proportions
Conditions for application are verified.

Discussion
This results shows equivalence for ACL’s complete diagnostics (for MRI and GNRB reports) with the literature and for incomplete ACL tears, it’s slightly lower than literature.
Sensibility’s results (for MRI and GNRB reports) for this study are equivalent for complete and partial tears diagnostic in the literature.
Conclusion
Sensibility of GNRB laximetry is quite the same than MRI for complete tears but superior for partial tears.
References
- Beldame J (2009) Etude radio-clinique du ligament croisé antérieur [Thèse de Doctorat en Médecine]. [France]. Université de Rouen Normandie.
- Lefevre N, Bohu Y, Naouri JF, Klouche S, Herman S (2014) Validity of GNRB® arthrometer compared to TelosTM in the assessment of partial anterior cruciate ligament tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22: 285–290. [Crossref]
- Klouche S, Lefevre N, Cascua S, Herman S, Gerometta A, Bohu Y (2015) Diagnostic value of the GNRB® in relation to pressure load for complete ACL tears: A prospective case-control study of 118 subjects. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 101: 297–300. [Crossref]
- Steltzlen C, Lefevre N, Bohu Y, Herman S (2011) Évaluation clinique d’une série continue de 55 cas de ligamentoplastie partielle du ligament croisé antérieur par la technique TLS (greffe courte aux ischio-jambiers). Rev Chir Orthopédique Traumatol 97: 493.
- Robert H, Nouveau S, Gageot S, Gagnière B (2009) A new knee arthrometer, the GNRB: Experience in ACL complete and partial tears. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 95: 171–176. [Crossref]