Trichoptera (Caddisflies) insects has long, silky hairs that cover most of the body and wings. This order of insect is included: 21 families, 145 Genera and 1200 species. This order is closely related to Lepidoptera. The Immature stage is aquatic and respiration at the larval stage by respiratory gills. Adults are active and winged insects and they have broad diversity of habitats. Larvae are worm-like, soft bodies, head contains a hard covering, color vary from yellow or brown, but usually green, larvae are known for their construction of hollow cases that they either carry with them or attach to rock, cases are built from sand, twigs, small stones, crushed shells, rolled leaves, and bark pieces, cases used for protection and pupation, length up to 1 inch. Larvae are Eruciform (caterpillar-like) body, abdomen usually enclosed in a case made of stones, leaves, twigs, or other natural materials.Head capsule well-developed with chewing mouthparts . Thread-like abdominal gills usually present in case-makers . They have one pair of hooked prolegs often present at tip of abdomen (Figure 1). larvae feed on algae,small bits of plant material . Some species build nets where they catch drifting food, fed upon by several species of fish. They are sensitive to water pollution and are used as important indicators in studies of water quality. The larval habitats are; lotic, lentic, erosional,warm rivers, headwater stream, cool streams, rock face streams, seeps, large rivers, small spring, marshland, small rapid stream, pond, pool, lake, temporary streams, depositional habitats, moss. The main habits of this insects are; clingers, burrowers, sprawlers, collectors, filterer, gatherer, scraper, predator (engulfers), shredder, herbivores, piercers, climbers, chewer (detritivore), scavenger, swimmer.
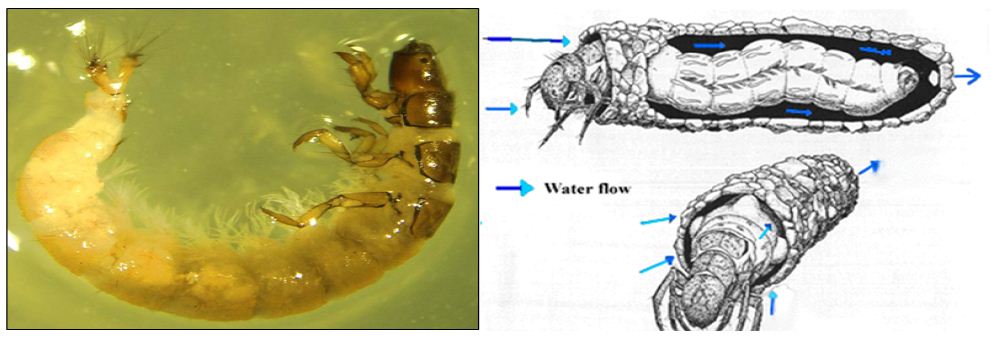
Figure 1: Larvae of Caddisfly
Caddisfly larvae best known for the construction of: nets, retreats and cases. Different types of larval cases are: smooth mineral, case flat, mineral tube with long plant pieces, tapered, flat tube of bark, sand construction case, case with stone, very slender case, case with wood fragments, snail shell shaped, flask shaped case, a tube of fine mineral, cylinder case, curved cylinder shape with wood pieces, tapered shape, irregular strands of vegetation, Christmas tree shape, curved cylinder of leaf pieces, square in cross-section, cylindrical of sand, rough mineral (Figure 2).
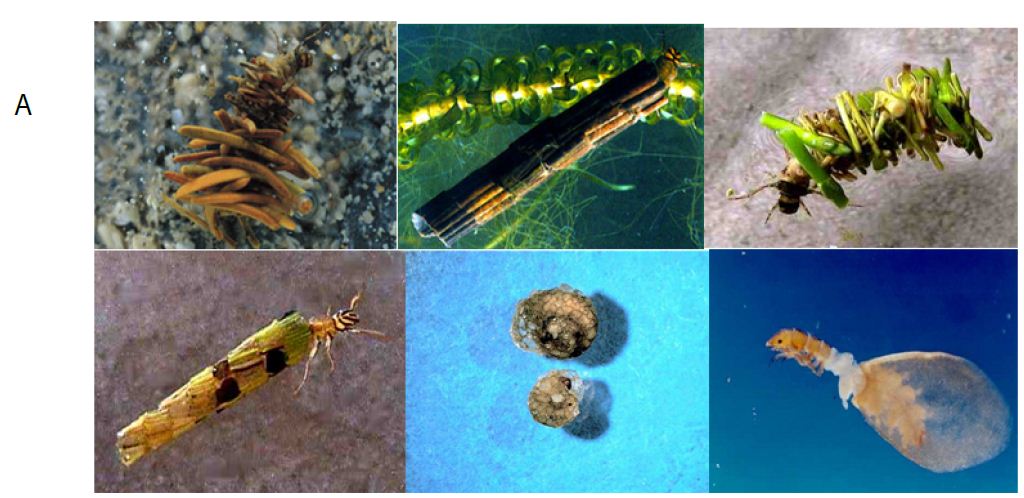
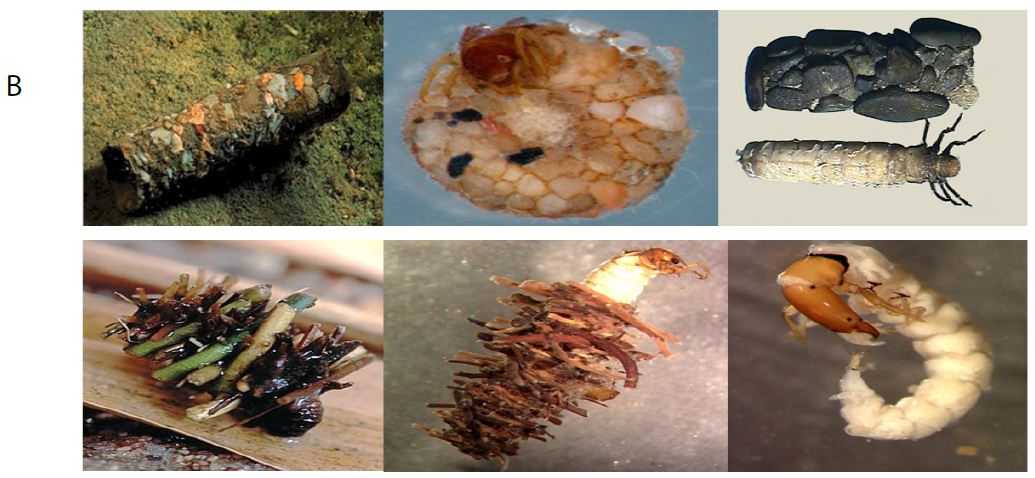
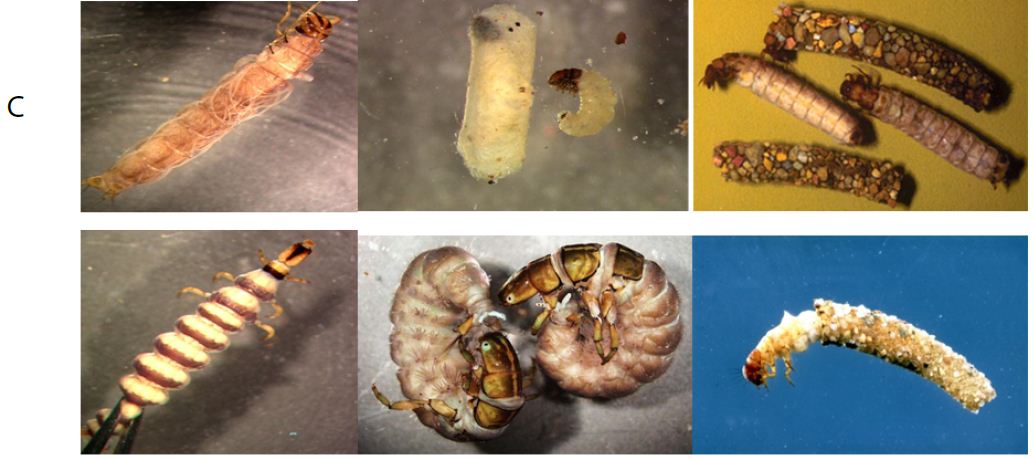
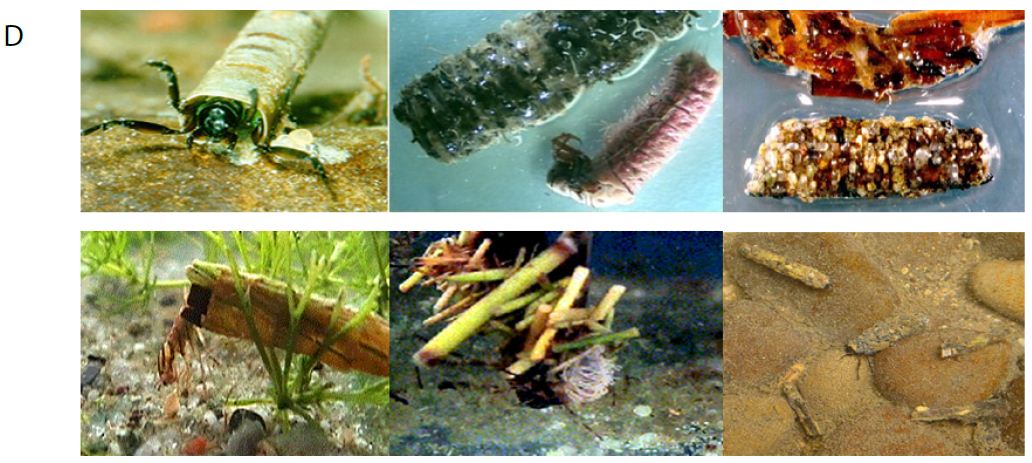
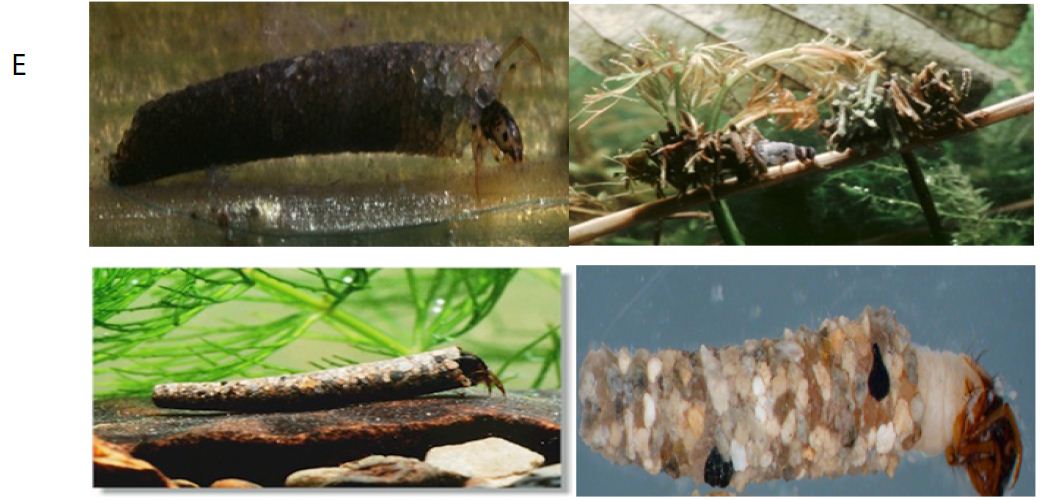






Figure 2: Different types of cases of caddisflies larvae
Larvae change to pupae (Figure 3).
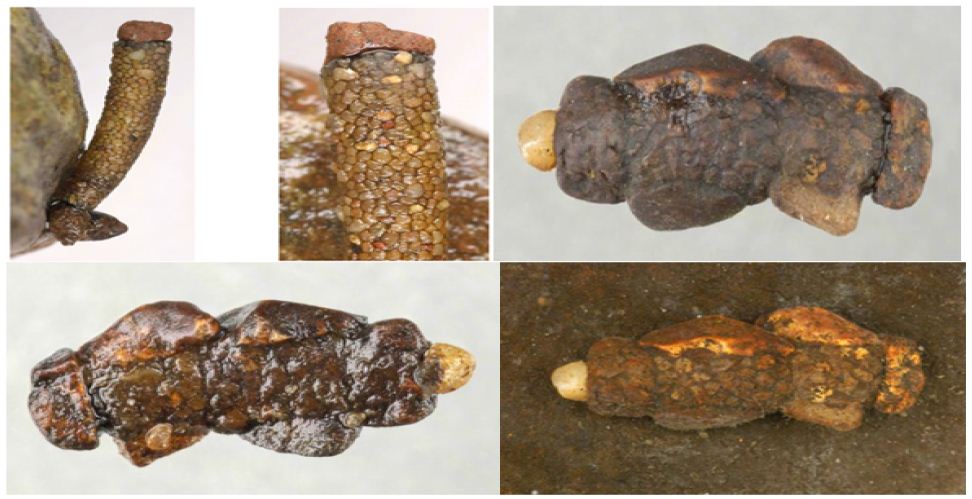

Figure 3: Pupae of Caddisflies
Adults are moth-like, brownish and usually nocturnal, wings thickly covered with hairs (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Adult of Caddisfly
Water Quality Indicators are: dissolved oxygen (do), phosphorus, coliform bacteria, turbidity, pH and macro-invertebrates. The presence, condition, and numbers of the types of Insects, can provide accurate information about the health of a specific river, stream, lake, wetland, or estuary. Cadissflies are being used as biological indicators for assessing water quality and good tools of physico-chemical properties of the water for classification. The most diverse group of freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates is the aquatic insects. Around 70% of known species of major groups of aquatic macro invertebrates were identified in North America. Around 4000 species of aquatic insects and water mites have been reported from Canada. Thus, as a highly diverse group, benthic macroinvertebrates are excellent candidates for studies of changes in biodiversity.